ATTENTION: The works hosted here are being migrated to a new repository that will consolidate resources, improve discoverability, and better show UTA's research impact on the global community. We will update authors as the migration progresses. Please see MavMatrix for more information.
Show simple item record
| dc.contributor.author | Guerrero, Nicolas Beltran | en_US |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2012-07-25T19:07:40Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2012-07-25T19:07:40Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2012-07-25 | |
| dc.date.submitted | January 2012 | en_US |
| dc.identifier.other | DISS-11728 | en_US |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10106/11017 | |
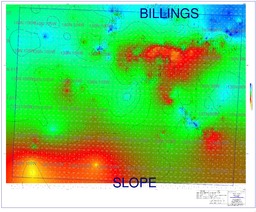
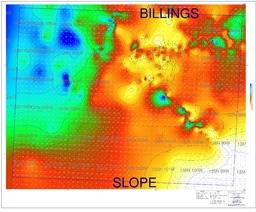
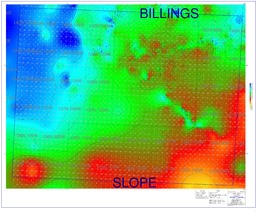
| dc.description.abstract | The purpose of this study is to investigate whether a correlation exists between surface lineaments and lithofacies distribution of the Pennsylvanian Tyler Formation in the southwest portion of North Dakota of the Williston Basin. If a cost-effective technique to locate preserved fluvial sandstone bodies can be developed, the Tyler Formation has the potential to be a productive hydrocarbon exploration target. Many intercratonic sedimentary basins, such as the Williston Basin, exhibit nearly orthogonal surface lineaments. In the case of the Cooper Basin in Australia, lineament analysis helped locate areas where Proterozoic rocks are fractured and filled with quartz veins containing precious metals. In the Michigan Basin, the lineament analysis helped locate deep faults that allow for greater heat flow among anticlinal structures and for thermogenic dolomite to develop. The dolomites are more likely to preserve secondary porosity and be reservoirs for oil. To locate areas with a greater probability of sandstone preservation, this North Dakota Tyler study attempts to establish the use of surface lineaments as a predictive indicator. The Tyler sandstones are presumably preferentially deposited along lineament orientations. The surface lineaments are the result of subtle topographic changes due to preferential erosion, minor structures, movement, and/or faults along weak zones in the basement rock. The basement weakness zones are reactivated throughout geologic history and should have resulted in lineaments during Pennsylvanian time. Fluvial morphology is highly susceptible to small topographic changes: consequently, Pennsylvanian surface lineaments should have bounded drainage pattern into the same orientation as present day surface lineaments. Unfortunately, surface lineament analysis alone did not find a correlation with known lithofacies distribution in the study area. | en_US |
| dc.description.sponsorship | Wickham, John | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | en | en_US |
| dc.publisher | Geology | en_US |
| dc.title | Surface Lineaments And Lithofacies Distribution Of The Tyler Formation In Southwestern North Dakota | en_US |
| dc.type | M.S. | en_US |
| dc.contributor.committeeChair | Wickham, John | en_US |
| dc.degree.department | Geology | en_US |
| dc.degree.discipline | Geology | en_US |
| dc.degree.grantor | University of Texas at Arlington | en_US |
| dc.degree.level | masters | en_US |
| dc.degree.name | M.S. | en_US |
Files in this item
- Name:
- Guerrero_uta_2502M_11728.pdf
- Size:
- 1.691Mb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate16_USRockies&Williston_Ed ...
- Size:
- 188.7Kb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- PLate17_TylerValleysWithFilled ...
- Size:
- 238.5Kb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate01_Grid_TylerUpperGross(N ...
- Size:
- 3.299Mb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate02_Grid_FryburgSandsoneGr ...
- Size:
- 3.113Mb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate03_Grid_TylerMidlleGross( ...
- Size:
- 2.656Mb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate04_Grid_TylerLowerGross(N ...
- Size:
- 3.694Mb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate05_Grid_TylerGross(NBG).pdf
- Size:
- 2.588Mb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate06_uppertylerCumulativesa ...
- Size:
- 117.4Kb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate07_MiddletylerCumulatives ...
- Size:
- 117.4Kb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate08_LowertylerCumulativesa ...
- Size:
- 142.6Kb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate09_Hillshadewithsurfaceli ...
- Size:
- 1.586Mb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate10_HillshadewithHistorica ...
- Size:
- 1.574Mb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate11_TylerValleyswithNEDLin ...
- Size:
- 101.2Kb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate12_TylerValleyswithLineam ...
- Size:
- 207.8Kb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate13_TylerCumulativesandsto ...
- Size:
- 146.4Kb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate14_Hillshadewithsurfaceli ...
- Size:
- 10.92Mb
- Format:
- PDF
- Name:
- Plate15_TylerValleyswithLineam ...
- Size:
- 211.2Kb
- Format:
- PDF
This item appears in the following Collection(s)
Show simple item record